What are mitochondria?
Mitochondria are specialized structures found in every cell of the human body. Commonly referred to as the "power plants" of cells, they are responsible for supplying cells with energy necessary to power all the functions and biochemical processes taking place in our bodies. As a result of cellular respiration, thanks to enzymes present in mitochondrial membranes, a huge amount of ATP, adenosine triphosphate - a carrier of chemical energy used in cell metabolism - is created inside mitochondria. The role of mitochondria in health and disease is enormous.
What are mitochondria responsible for?
Effective mitochondria means optimal health. Mitochondria also:
play a fundamental role in the aging process and most age-related diseases
contain their own DNA, which is easily damaged, susceptible to mutations and has a limited ability to be repaired
play a key role in the functioning of all systems, including the immune system.
As our environment becomes more polluted, the quality of our food decreases, and the number of medications people take increases, the quality of our mitochondria is also deteriorating. The good news is that we can do a lot to change this. There are ways, including lifestyle changes, that can be very effective in supporting mitochondrial health and function.
How to support mitochondrial health?
Mitochondria are particularly susceptible to oxidative damage, nutrient deficiencies and environmental toxins.
Reduction of oxidative stress
Oxidative stress is a situation in which the amount of free oxygen radicals exceeds the body's ability to neutralize them. Excessive free radicals cause both DNA damage and trigger pro-inflammatory or pro-carcinogenic signaling pathways and promote the intensification of aging processes. In order to reduce antioxidant stress, you should take care of a proper diet and take a preventive approach to all inflammatory conditions, but also - avoid harmful environmental factors that increase the level of this type of stress in the body (tobacco smoke, electrosmog, harmful sunlight).
The right amount of calories and nutrients
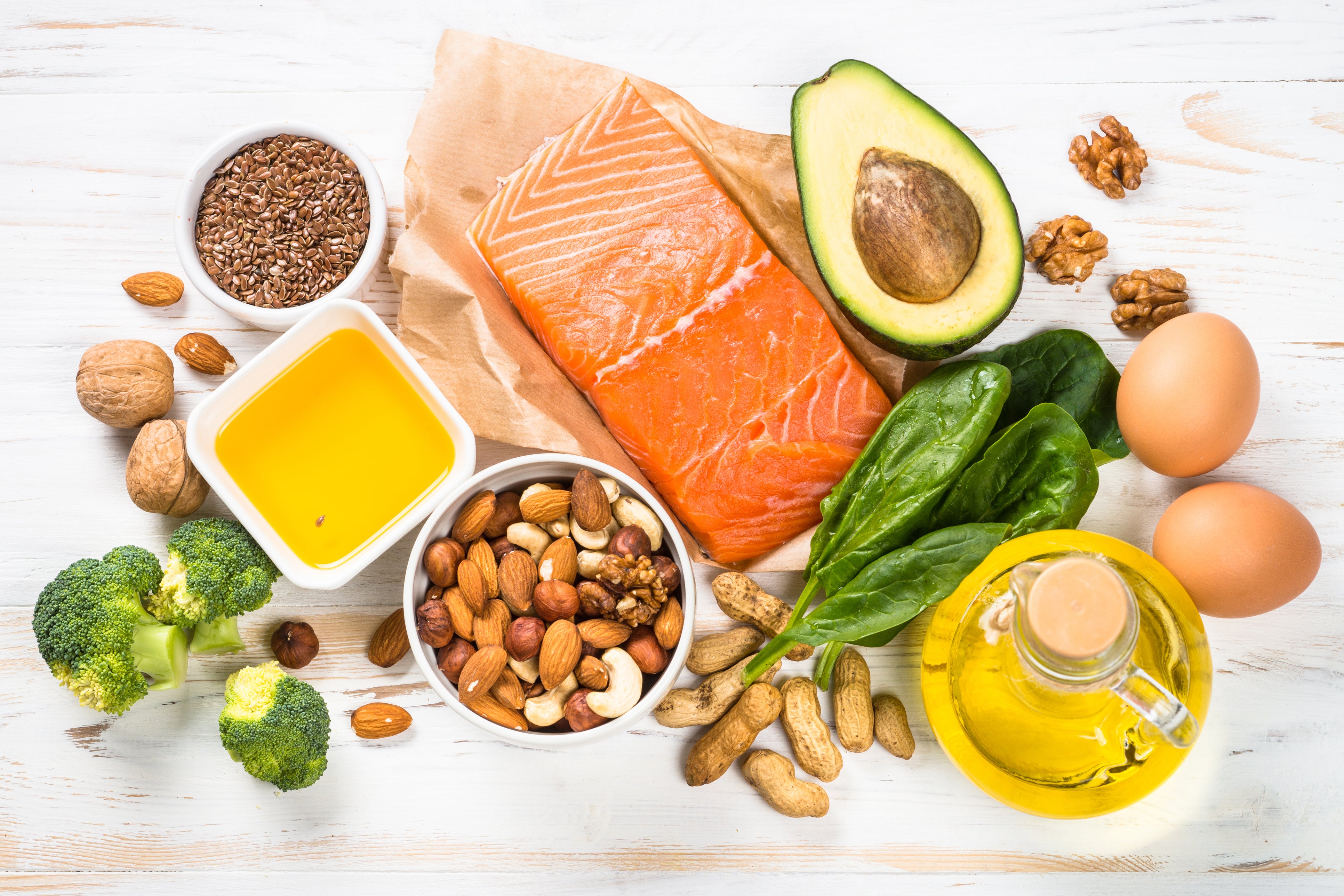
Mitochondria benefit from avoiding sugar and processed foods and eating a diet rich in:
• Antioxidants
• B vitamins
• Sulfur
• Fats
• Magnesium
There are also studies that have shown that mitochondria are beneficial when calorie restriction occurs.
Regular physical activity
Increasing the number of mitochondria provides energy, vitality and delays the aging process. Studies show that high-intensity interval training combined with strength training is a good way to create new, improved mitochondria. This is because for physical exertion, muscles need an increased amount of ATP energy produced in mitochondria.
However, for physical activity to really benefit us, it should be individually tailored. Poorly selected, too intense physical activity can lead to mitochondrial overload and serious damage.
As we age, mitochondrial quality and activity decline, but regardless of age, the condition of our mitochondria influences or regulates many key aspects of our health and the rate of aging. A decline in healthy mitochondria promotes damage at the cellular, tissue and organ levels and accelerates aging.
Take care of your mitochondria! Even if you have an unfavorable genetic predisposition, you can control it by choosing a healthy diet and lifestyle.